|
|
|
|
| When a person is
giving a lecture or speech, information is primarily conveyed in one
direction. Duration a conversation between two person, how ever, spoken
messages (information) are usually exchanged in both directions. These
messages are normally exchanged alternately but, can of course, be
exchanged simultaneously! Similarly, when data is transmitted between
two pieces of equipment, three analogous modes of operation can be used: |
|
| Three types of
Data Transmission: |
 |
- Simplex
- Half-Duplex
- Full-Duplex
|
|
BACK
TO TOP |
|
|
|
| Data in a Simplex
transmission is always one way. Simplex transmission are not often used
because it is not possible to send back error or control signals to the
transmit end. |
|
|
It's like
a one-way street. An example of simplex is sTelevision, or Radio.
|
|
|
|
|
|
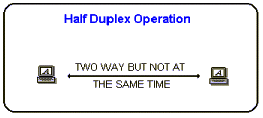
| A half-duplex
transmission can send and receive in one direction, but not at the same
time. It's like a one-lane bridge where two-way traffic must give way
in
order to cross. Only one end transmits at a time, the other end
receives. In addition, it is possible to perform error detection and
request the sender to retransmit information that arrived corrupted. In
some aspects, you can think of Internet surfing as being half-duplex,
as a user issues a request for a web document, then that document is
downloaded and displayed before the user issues another request. |
|
|
|
Another example of
half-duplex is talkback radio, and CB Radio (Citizens Band). You might
have seen movies where a truck driver (drivers of very big trucks)
communicates to each other, and when they want the other person to
speak
they say "over". This is because only one person can talk at a time
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
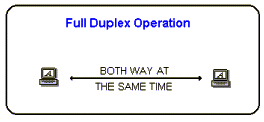
| Data can travel in
both directions simultaneously. There is no need to switch from
transmit
to receive mode like in half duplex. It like a two lane bridge on a
two-lane highway. Have you ever watched these television talk shows
where the host has a number of people on the show, and they all try to
talk at once. Well, that's full duplex! |
|
|
Of course,
in the world of data communications, full duplex allows both way
communications simultaneously. An example can be a consumer, which uses
a cable connection not only, receives TV channels, but also the same
cable to support their phone and Internet surfing. All these activities
can occur simultaneously.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
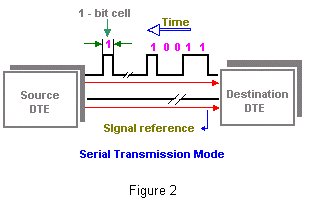
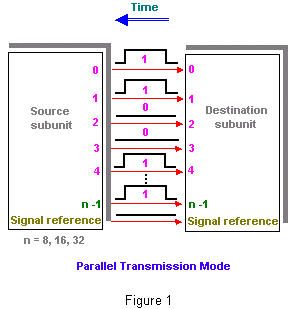
| In figure 1 and 2,
A high signal relative to the reference indicates the transmission of
Binary 1 while a low signal level, equal to the reference, represents a
binary 0. With serial transmission the high-and low-level signals are
normally positive and negative voltages relative to the reference. |
|
|
|
| Data Transmission Speed |
|
|
|
|
|
|